HPE6-A84 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is migrating from on-prem AD to Azure AD as its sole domain solution. The customer also manages both wired and wireless devices with Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune).
The customer wants to improve security for the network edge. You are helping the customer design a ClearPass deployment for this purpose. Aruba network devices will authenticate wireless and wired clients to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster (which uses version 6.10).
The customer has several requirements for authentication. The clients should only pass EAP-TLS authentication if a query to Azure AD shows that they have accounts in Azure AD. To further refine the clients' privileges, ClearPass also should use information collected by Intune to make access control decisions.
Assume that the Azure AD deployment has the proper prerequisites established.
You are planning the CPPM authentication source that you will reference as the authentication source in 802.1X services.
How should you set up this authentication source?
A. As Kerberos type
B. As Active Directory type
C. As HTTP type, referencing the Intune extension
D. AS HTTP type, referencing Azure AD's FODN
A customer's admins have added RF Protect licenses and enabled WIDS for a customer's AOS 8-based solution. The customer wants to use the built-in capabilities of APs without deploying dedicated air monitors (AMs). Admins tested rogue AP detection by connecting an unauthorized wireless AP to a switch. The rogue AP was not detected even after several hours.
What is one point about which you should ask?
A. Whether APs' switch ports support all the VLANs that are accessible at the edge
B. Whether admins enabled wireless containment
C. Whether admins set at least one radio on each AP to air monitor mode
D. Whether the customer is using non-standard Wi-Fi channels in the deployment
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network infrastructure devices.
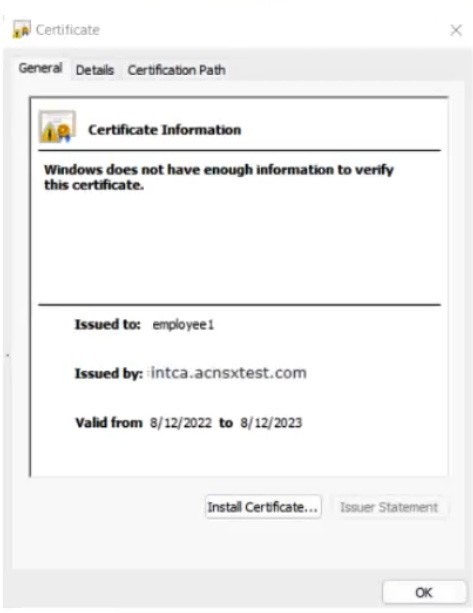
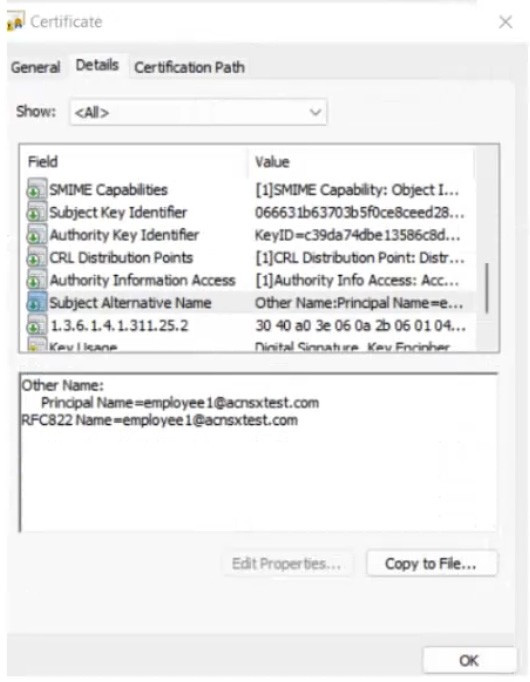
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows CA. The Window CA issues certificates to domain computers, domain users, and servers such as domain controllers. An example of a certificate issued by the Windows CA is shown here.
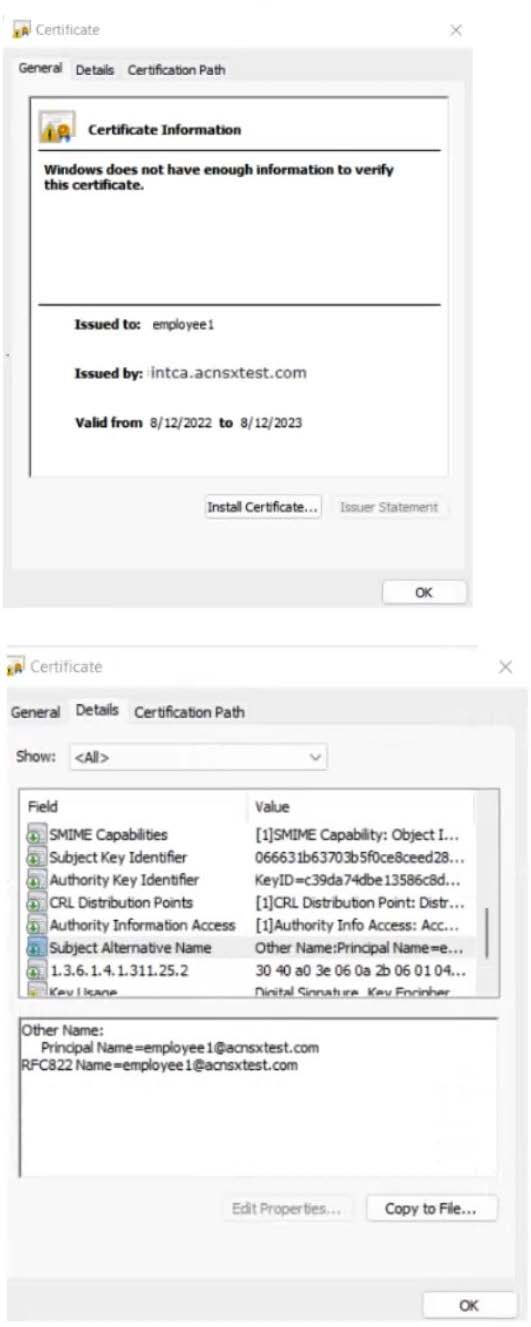
The company is in the process of adding Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) to manage its mobile clients. The customer is maintaining the on-prem AD for now and uses Azure AD Connect to sync with Azure AD.
# Requirements for issuing certificates to mobile clients
The company wants to use ClearPass Onboard to deploy certificates automatically to mobile clients enrolled in Intune. During this process, Onboard should communicate with Azure AD to validate the clients. High availability should also be
provided for this scenario; in other words, clients should be able to get certificates from Subscriber 2 if Subscriber 1 is down.
The Intune admins intend to create certificate profiles that include a UPN SAN with the UPN of the user who enrolled the device.
# Requirements for authenticating clients
The customer requires all types of clients to connect and authenticate on the same corporate SSID.
The company wants CPPM to use these authentication methods:
1.
EAP-TLS to authenticate users on mobile clients registered in Intune
2.
TEAR, with EAP-TLS as the inner method to authenticate Windows domain computers and the users on them To succeed, EAP-TLS (standalone or as a TEAP method) clients must meet these requirements:
1.
Their certificate is valid and is not revoked, as validated by OCSP
2.
The client's username matches an account in AD
# Requirements for assigning clients to roles
After authentication, the customer wants the CPPM to assign clients to ClearPass roles based on the following rules:
1.
Clients with certificates issued by Onboard are assigned the "mobile-onboarded" role
2.
Clients that have passed TEAP Method 1 are assigned the "domain-computer" role
3.
Clients in the AD group "Medical" are assigned the "medical-staff" role
4.
Clients in the AD group "Reception" are assigned to the "reception-staff" role
The customer requires CPPM to assign authenticated clients to AOS firewall roles as follows:
1.
Assign medical staff on mobile-onboarded clients to the "medical-mobile" firewall role
2.
Assign other mobile-onboarded clients to the "mobile-other" firewall role
3.
Assign medical staff on domain computers to the "medical-domain" firewall role
4.
All reception staff on domain computers to the "reception-domain" firewall role
5.
All domain computers with no valid user logged in to the "computer-only" firewall role
6.
Deny other clients access
# Other requirements
Communications between ClearPass servers and on-prem AD domain controllers must be encrypted.
# Network topology
For the network infrastructure, this customer has Aruba APs and Aruba gateways, which are managed by Central. APs use tunneled WLANs, which tunnel traffic to the gateway cluster. The customer also has AOS-CX switches that are not managed by Central at this point.
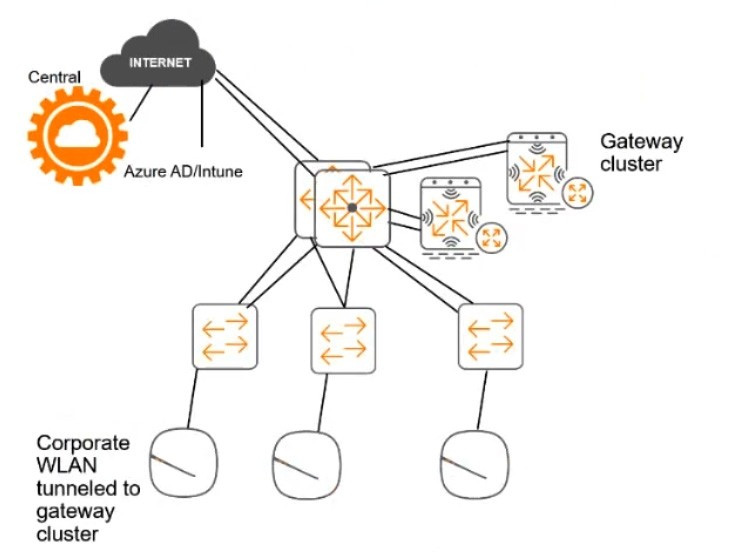
# ClearPass cluster IP addressing and hostnames
A customer's ClearPass cluster has these IP addresses:
1.
Publisher = 10.47.47.5
2.
Subscriber 1 = 10.47.47.6
3.
Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.7
4.
Virtual IP with Subscriber 1 and Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.8
The customer's DNS server has these entries
1.
cp.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.5
2.
cps1.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.6
3.
cps2.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.7
4.
radius.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
5.
onboard.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
You have started to create a CA to meet the customer's requirements for issuing certificates to mobile clients, as shown in the exhibit below.
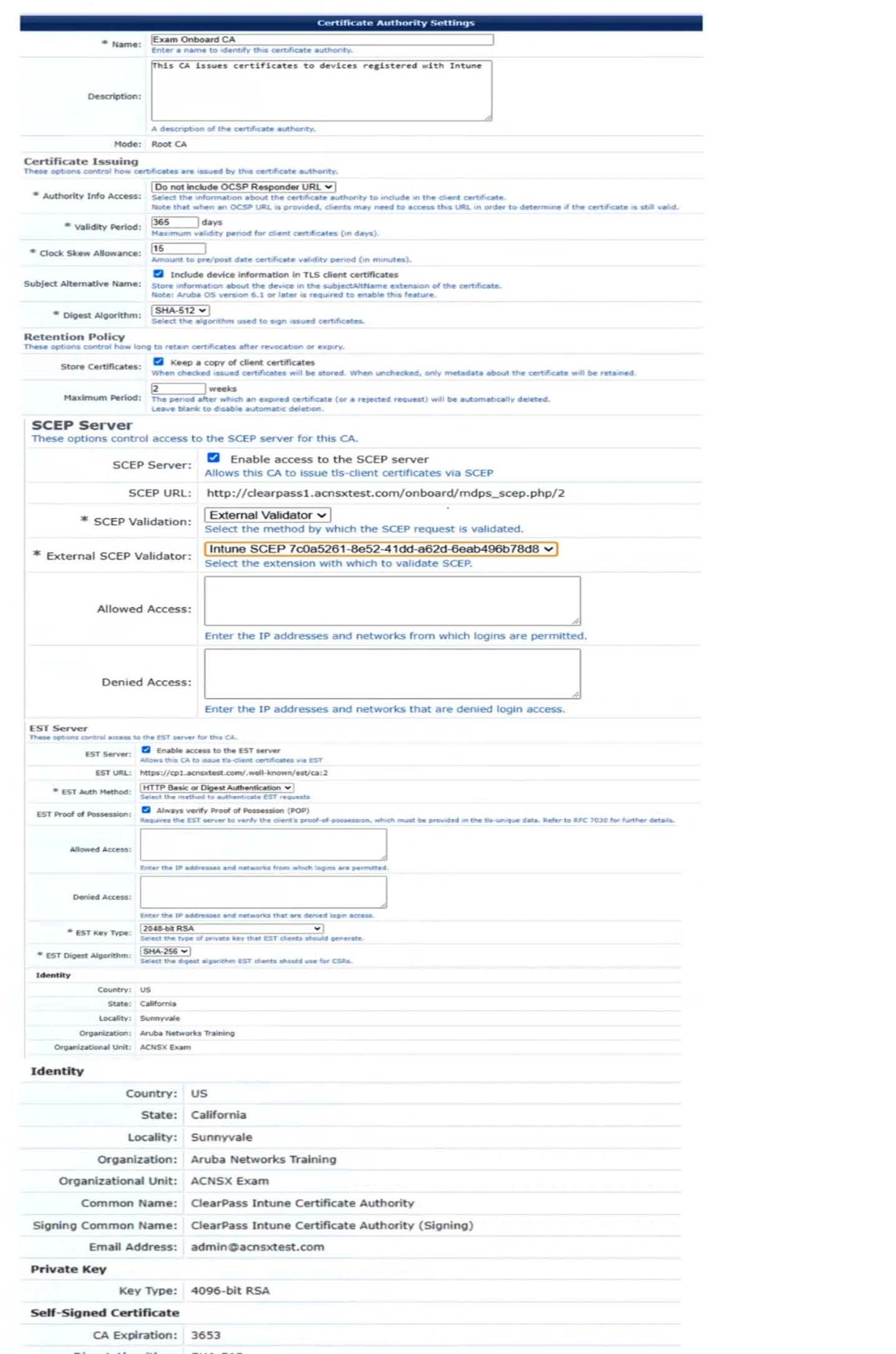
What change will help to meet those requirements and the requirements for authenticating clients?
A. Change the EST authentication method to use an external validator.
B. Change the EST Digest Algorithm to SHA-512.
C. Recreate the CA as a registration authority under Azure AD.
D. Specify an OCSP responder, setting the hostname to localhost.
Refer to the exhibit.
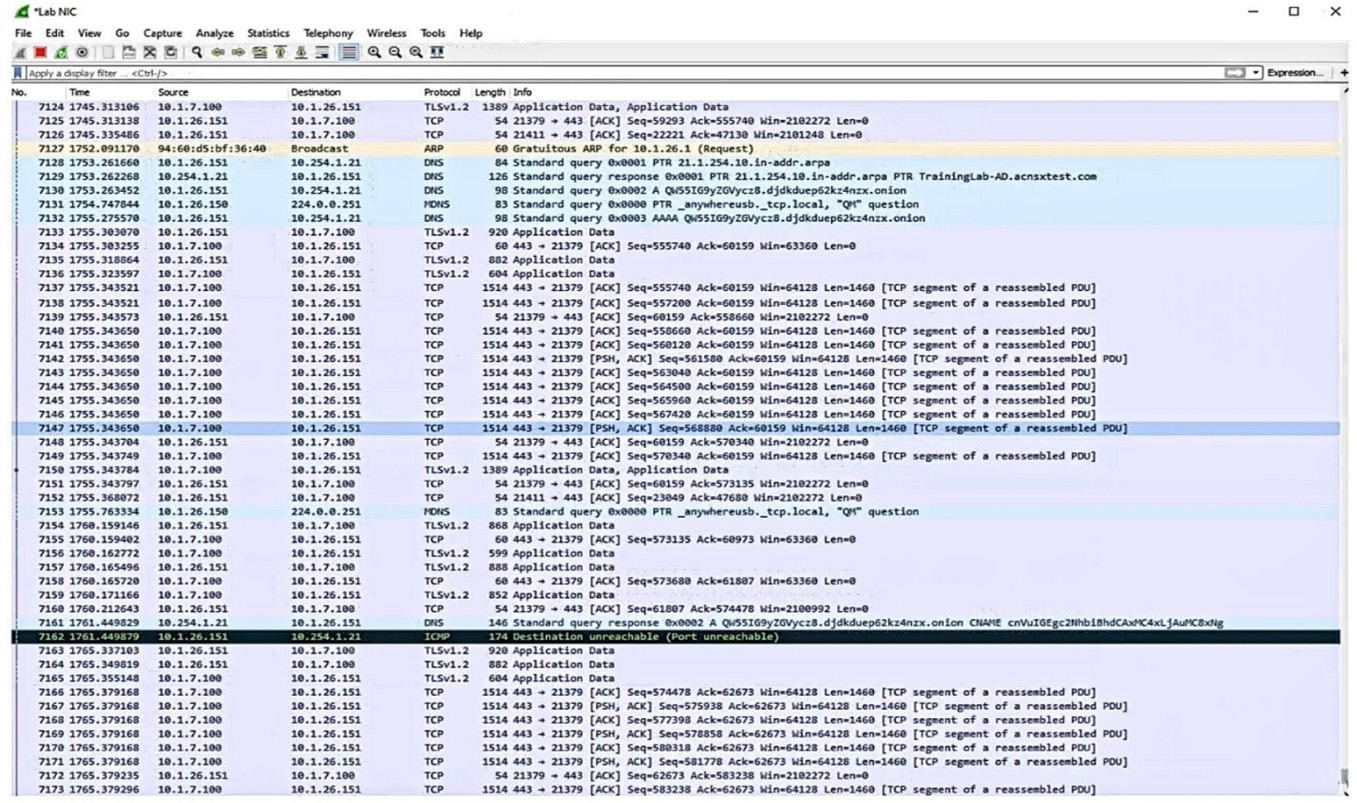
Which IP address should you record as a possibly compromised client?
A. 10.1.26.151
B. 10.1J.100
C. 10.1.26.1
D. 10.254.1.21
Refer to the scenario.
# Introduction to the customer
You are helping a company add Aruba ClearPass to their network, which uses Aruba network infrastructure devices.
The company currently has a Windows domain and Windows CA. The Window CA issues certificates to domain computers, domain users, and servers such as domain controllers. An example of a certificate issued by the Windows CA is shown here.
The company is in the process of adding Microsoft Endpoint Manager (Intune) to manage its mobile clients. The customer is maintaining the on-prem AD for now and uses Azure AD Connect to sync with Azure AD.
# Requirements for issuing certificates to mobile clients
The company wants to use ClearPass Onboard to deploy certificates automatically to mobile clients enrolled in Intune. During this process, Onboard should communicate with Azure AD to validate the clients. High availability should also be
provided for this scenario; in other words, clients should be able to get certificates from Subscriber 2 if Subscriber 1 is down.
The Intune admins intend to create certificate profiles that include a UPN SAN with the UPN of the user who enrolled the device.
# Requirements for authenticating clients
The customer requires all types of clients to connect and authenticate on the same corporate SSID.
The company wants CPPM to use these authentication methods:
1.
EAP-TLS to authenticate users on mobile clients registered in Intune
2.
TEAR, with EAP-TLS as the inner method to authenticate Windows domain computers and the users on them To succeed, EAP-TLS (standalone or as a TEAP method) clients must meet these requirements:
1.
Their certificate is valid and is not revoked, as validated by OCSP
2.
The client's username matches an account in AD # Requirements for assigning clients to roles After authentication, the customer wants the CPPM to assign clients to ClearPass roles based on the following rules:
1.
Clients with certificates issued by Onboard are assigned the "mobile-onboarded" role
2.
Clients that have passed TEAP Method 1 are assigned the "domain-computer" role
3.
Clients in the AD group "Medical" are assigned the "medical-staff" role
4.
Clients in the AD group "Reception" are assigned to the "reception-staff" role The customer requires CPPM to assign authenticated clients to AOS firewall roles as follows:
1.
Assign medical staff on mobile-onboarded clients to the "medical-mobile" firewall role
2.
Assign other mobile-onboarded clients to the "mobile-other" firewall role
3.
Assign medical staff on domain computers to the "medical-domain" firewall role
4.
All reception staff on domain computers to the "reception-domain" firewall role
5.
All domain computers with no valid user logged in to the "computer-only" firewall role
6.
Deny other clients access # Other requirements Communications between ClearPass servers and on-prem AD domain controllers must be encrypted. # Network topology For the network infrastructure, this customer has Aruba APs and Aruba gateways, which are managed by Central. APs use tunneled WLANs, which tunnel traffic to the gateway cluster. The customer also has AOS-CX switches that are not
managed by Central at this point.

# ClearPass cluster IP addressing and hostnames A customer's ClearPass cluster has these IP addresses:
1.
Publisher = 10.47.47.5
2.
Subscriber 1 = 10.47.47.6
3.
Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.7
4.
Virtual IP with Subscriber 1 and Subscriber 2 = 10.47.47.8
The customer's DNS server has these entries
1.
cp.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.5
2.
cps1.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.6
3.
cps2.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.7
4.
radius.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
5.
onboard.acnsxtest.com = 10.47.47.8
You have imported the root certificate for the Windows CA to the ClearPass CA Trust list.
Which usages should you add to it based on the scenario requirements?
A. EAP and AD/LDAP Server
B. LDAP and Aruba infrastructure
C. Radsec and Aruba infrastructure
D. EAP and Radsec
How does Aruba Central handle security for site-to-site connections between AOS 10 gateways?
A. It uses an Aruba proprietary integrity and encryption technologies to secure site-to-site connections, making them resistant to zero day attacks.
B. It automatically establishes IPsec tunnels for all site-to-site (all HUBs and Branches) connections using keys securely distributed by Central.
C. It automatically steers traffic away from Internet-based connections to more secure MPLS connections to reduce encryption overhead.
D. It automatically establishes simple-to-manage and highly secure TLSv1.3 tunnels between gateways.
A customer has an AOS 10-based solution, including Aruba APs. The customer wants to use Cloud Auth to authenticate non-802.1X capable IoT devices.
What is a prerequisite for setting up the device role mappings?
A. Configuring a NetConductor-based fabric
B. Configuring Device Insight (client profile) tags in Central
C. Integrating Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) and Device Insight
D. Creating global role-to-role firewall policies in Central
Refer to the scenario.
A hospital has an AOS10 architecture that is managed by Aruba Central. The customer has deployed a pair of Aruba 9000 Series gateways with Security licenses at each clinic. The gateways implement IDS/IPS in IDS mode.
The Security Dashboard shows these several recent events with the same signature, as shown below:

Which step could give you valuable context about the incident?
A. View firewall sessions on the APs and record the threat sources' type and OS.
B. View the user-table on APs and record the threat sources' 802.11 settings.
C. View the RAPIDS Security Dashboard and see if the threat sources are listed as rogues.
D. Find the Central client profile for the threat sources and note their category and family.
Refer to the scenario.
A customer has an AOS10 architecture that is managed by Aruba Central. Aruba infrastructure devices authenticate clients to an Aruba ClearPass cluster.
In Aruba Central, you are examining network traffic flows on a wireless IoT device that is categorized as "Raspberry Pi" clients. You see SSH traffic. You then check several more wireless IoT clients and see that they are sending SSH also. You want a fast way to find a list of all the IoT clients that have used SSH.
What step can you take?
A. Create and apply a Central client profile tag that selects the SSH application and the clients' category.
B. Run a search for SSH traffic and loT client IDs in Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager's (CPPM's) accounting information.
C. Use Central's Live Events monitoring tool to detect which clients meet the desired criteria.
D. Use Central's Gateway IDS/IPS Security Dashboard to search for SSH events and sources.
Refer to the scenario.
A customer is using an AOS 10 architecture with Aruba APs and Aruba gateways (two per site). Admins have implemented auto-site clustering for gateways with the default gateway mode disabled. WLANs use tunneled mode to the gateways.
The WLAN security is WPA3-Enterprise with authentication to an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager (CPPM) cluster VIP. RADIUS communications use RADIUS, not RadSec.
CPPM is using the service shown in the exhibits.
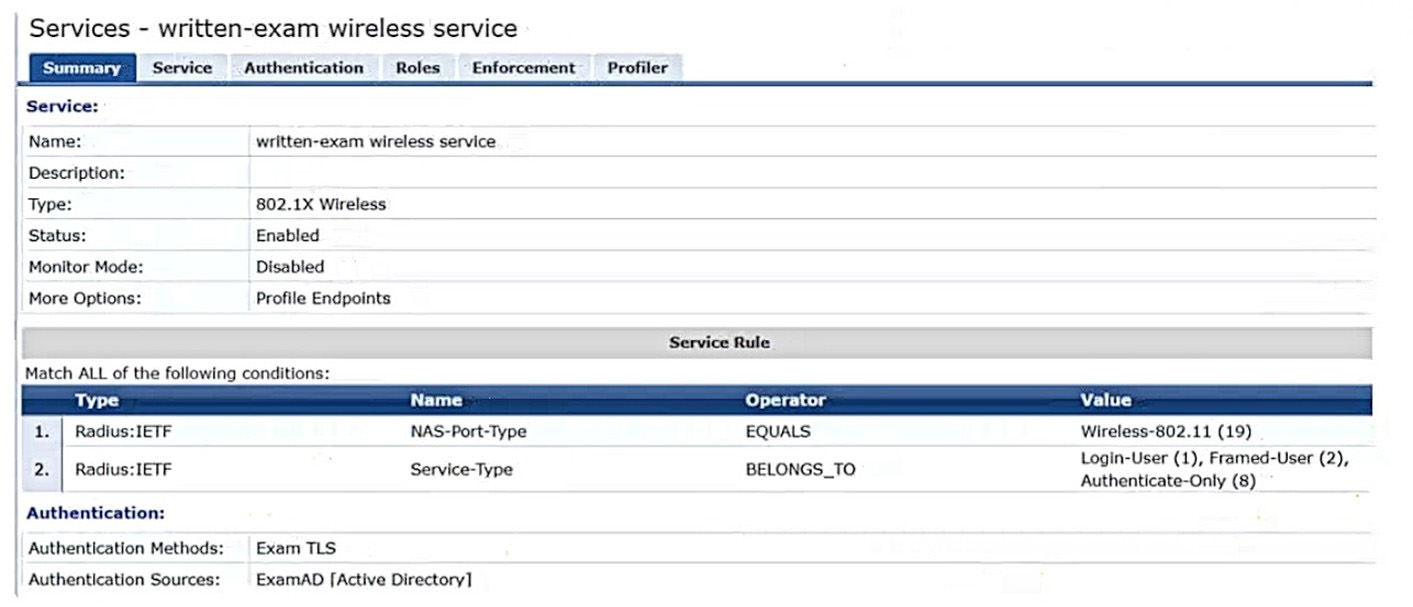
Which step can you take to improve operations during a possible gateway failover event?
A. Chanqe the WLANs to mixed-mode forwardinq so that vou can select multiple qatewav clusters.
B. Set up qatewav clusters manually and set VRRP IP addresses for dynamic authorization.
C. Use auto-group clustering instead of auto-site clustering for the gateways.
D. Enable default gateway mode for the gateway clusters.

