HPE6-A42 Online Practice Questions and Answers
What is a requirement for the Dashboard > Traffic Analysis window on the Aruba Mobility Master (MM) to show data?
A. Airmatch and ClientMatch must be enabled.
B. The solution must have active PEFNG licenses.
C. Firewall policies must include application filtering rules.
D. WLANs must use the decrypt-tunnel forwarding option.
Refer to the exhibit.
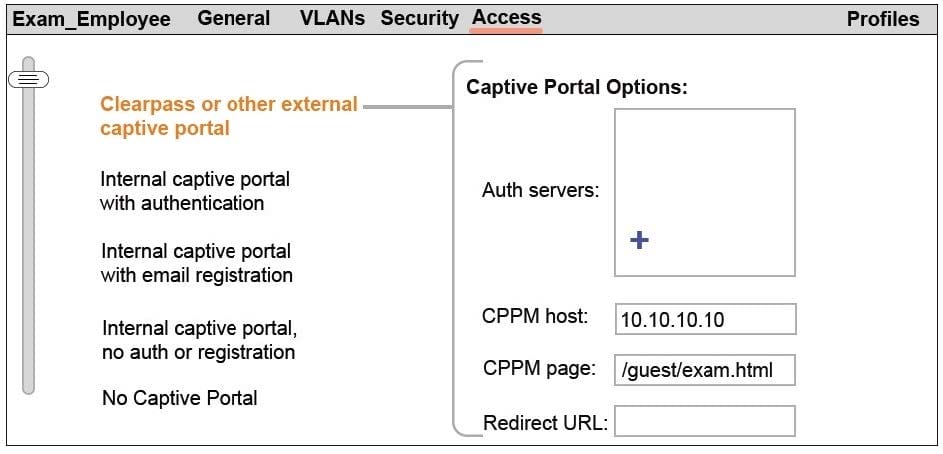
A network administrator creates a guest WLAN on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM). The exhibit shows some of the settings for the WLAN.
How should the network administrator handle the Auth server settings?
A. Add an authentication server with the LDAP type and the IP address of the company AD server.
B. Add an authentication server with the LDAP type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
C. Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and IP address 10.10.10.10.
D. Add an authentication server with the RADIUS type and the IP address of the company AD server.
Network administrators use the wizard to create a WLAN that uses WPA2-Enterprise security to a RADIUS server at 10.21.98.55. They do not manually change any settings.
Which device determines the EAP type that the wireless clients must support?
A. Mobility Master (MM)
B. Mobility Controller (MC)
C. RADIUS server
D. AP
A network administrator configures an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)-based solution to provide wireless access to employees. The solution must meet these criteria:
Authenticate users to a network RADIUS server
Enforce different Aruba firewall rules based on the user department
How can the administrator meet these criteria in the simplest way?
A. Have the RADIUS server assign users in different departments to different VLANs. Apply firewall policies based on IP ranges.
B. Have the RADIUS server send different roles for users in different departments. Apply role-based firewall policies.
C. Create multiple zones on the MM. Assign different departments and sets of firewall policies to different zones.
D. Create a different WLAN and SSID for each department. Apply different firewall policies to each WLAN.
What is one reason for a network administrator to visit the Dashboard > Usage window on an Aruba Mobility Master (MM)?
A. to check license usage and determine the need for additional licenses
B. to analyze short terms trends in network usage by client, AP, and application
C. to view system usage statistics for the MM and troubleshoot potential issues
D. to generate reports about traffic patterns and network usage over the past several months
A company plans to deploy a Mobility Master (MM) solution with two MM nodes. The MM solution will manage 20 Mobility Controller (MC) appliances that will control a total of 800 APs.
How should the network administrator install the AP licenses?
A. 40 AP licenses on the MM
B. 400 AP licenses on the MM
C. 800 AP licenses on each MC
D. 800 AP licenses on the MM and 40 AP licenses on each MC
A network administrator uses a wireless intrusion detection system (WIDS) to detect 802.11 association floods. At which layer do these attacks occur?
A. Layer 1
B. Layer 2
C. Layer 3
D. Layer 7
A network administrator examines a list of 2.4GHz clients with low performance in the Mobility Master (MM) dashboard. Which property for a client should pose a concern as a potential performance issue?
A. Radio PHY of HT 20MHz
B. Max speed of 72Mbps
C. Goodput data rate of 12 Mbps
D. Usage of 10 MB
For which use case should network administrators set up Aruba access points (APs) as multi-zone APs?
A. The company has multiple small branch offices where APs at each branch office must forward internet traffic locally and corporate traffic over a secure tunnel to a centralized Mobility Controller (MC).
B. The company has some devices that support both 5GHz and 2.4GHz, and the APs must operate in both frequency bands.
C. The company requires high availability for its wireless services, and APs must be able to be controlled by more than one Mobility Controller (MC) in case a controller fails.
D. The company has a Mobility Manager (MM)-based solution that requires APs to terminate to multiple controllers that reside in different administrative domains.
A company has many 7220 controllers in its Aruba wireless architecture. A network administrator wants to use the Traffic Analysis dashboard in order to monitor which type of applications is being used by wireless users.
What is required for this implementation?
A. Airmatch and ClientMatch must be enabled.
B. The solution must have active PEFNG licenses.
C. Firewall policies must include application filtering rules.
D. WLANs must use the decrypt-tunnel forwarding option.

