CTAL-TM_SYLL2012 Online Practice Questions and Answers
You are the Test Manager for a project to develop a web customer portal of a Pay-TV company that allows customers (with a smartcard and a set-top box) to purchase digital contents.
In the "select" page the system displays a dialogue where the customer can select the items (digital contents) he/she is interested in. In this page he/she can add one or more items to a shopping cart. An item consists of a product and a
duration.
There are three types of products: Movie, sport and premium (movie and sport).
There are four possible durations: 1 months, 2 months, winter (from the beginning of January to end of March) and summer (from the beginning of July to end of September).
All the combinations of products and durations are allowed to define an item. Thus there are twelve possible items. A maximum of six different items can be added to the shopping cart at a time.
When the customer decides to check out he/she goes to the "purchase" page where he/she can pay the total amount of the shopping cart in three different ways:
-
using a credit voucher
-
using a credit already charged on the smartcard
-
using a credit card (accepted credit cards are. Visa, MasterCard and Great Wall Card)
The customer can logout from both the "select" and "purchase" pages. In this case no purchase is made.
You decide to apply a blended risk-based and reactive testing strategy and the following is a subset of the exit criteria for system testing:
EXCR1- Each "critical" quality risk item must be covered by at least one test condition
EXCR2- Each "critical" requirement must be covered by at least one test condition
You are following a risk-based testing strategy. The test execution time is very limited. Assume that all the product risk items require more or less the same level of test effort.
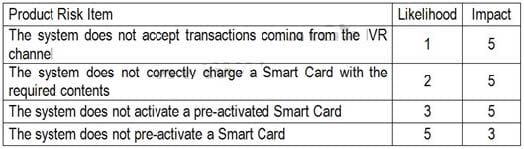
Which of the following answers describes the best execution schedule in this scenario?
A. 1- Test the acceptance of transactions coming from the IVR channel 2- Test the correct charge of the Smart Card with the required contents 3- Test the correct pre-activation of the Smart Card 4- Test the correct activation of the Smart Card
B. 1- Test the correct pre-activation of the Smart Card 2- Test the correct charge of the Smart Card with the required contents 3- Test the correct activation of the Smart Card 4- Test the acceptance of transactions coming from the IVR channel
C. 1- Test the correct activation of the Smart Card 2- Test the correct pre-activation of the Smart Card 3- Test the correct charge of the Smart Card with the required contents 4- Test the acceptance of transactions coming from the IVR channel
D. 1- Test the correct pre-activation of the Smart Card 2- Test the correct activation of the Smart Card 3- Test the correct charge of the Smart Card with the required contents 4- Test the acceptance of transactions coming from the IVR channel
Which of the following statements about management of product quality risks in mature organizations with respect to the lifecycle, is true?
A. Mature organizations address product quality risks associated to non-functional characteristics only during the system test phase
B. Mature organizations are aware that the contribution of testing to analysis of product quality risks is very important. The analysis should occur throughout the entire lifecycle
C. Mature organizations don't waste time identifying the sources of risks. They only focus on identifying product quality risks
D. Mature organizations are aware that risk management of product quality risks only occurs during testing
Assume you are currently working on a project developing a system where functional requirements are very well specified. Unfortunately non-functional requirements do almost not exist.
You are the Test Manager. You have to choose a technique for test selection that allows testing of non-functional characteristics, especially reliability.
Which of the following techniques for test selection do you expect being most useful in this scenario?
A. A model-based technique based on the creation of operational profiles
B. Ambiguity reviews
C. Test condition analysis
D. Cause-effect graphing
Consider the following list of statements about audits and management reviews:
I. Audits are usually more effective than management reviews at finding defects
II. Audits and management reviews have the same main goals, the only difference is related to the roles and level of formality
III. A typical outcome of an audit includes observations and recommendations, corrective actions and a pass/fail assessment
IV.
An audit is not the appropriate mechanism to use at the code review in order to detect defects prior to dynamic testing Which of the following statements is true?
A.
I. and III. are true; II. and IV. are false;
B.
II. and III are true; I. and IV. are false;
C.
III. and IV. are true; I and II are false;
D.
I, III and IV are true; II. is false;
Assume you are working on a defect management process to be used by a software organization to track the current status of the defects reports for several projects.
When a defect is found for investigation a defect report is created in "Opened" state that is the unique initial state. The defect report status has also a unique finale state that is the "Closed" state.
The following state transition diagram describes the states of this defect management process:
Where only the initial ("Opened") and final ("Closed") states are indicated while the remaining states (V, W, X, Y, Z) have yet to be named.
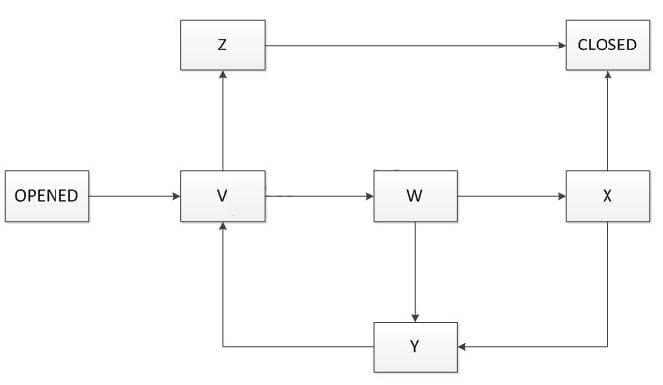
Which of the following assignments would you expect to best complete the defect management process?
A. V=Rejected , W=Corrected , X=Validated, Y=Re-Opened, Z=Assigned
B. V=Assigned, W=Validated , X=Corrected, Y=Re-Opened, Z=Rejected
C. V=Assigned, W=Corrected , X=Validated, Y=Re-Opened, Z=Rejected
D. V= Corrected, W=Assigned, X=Validated, Y=Corrected, Z=Rejected
During the system testing phase a tester from your test team observes a failure in the system under test and he/she decides to create an incident report. The incident report is currently in a "new" state, indicating it needs to be investigated. Which THREE of the following information items can't yet be present in the incident report?
A. The type of defect that caused the failure
B. The actual and the expected result highlighting the failure
C. The lifecycle phase in which the defect has been introduced
D. What really caused the failure (actual cause)
E. Steps to reproduce the failure, including screenshots, database dumps and logs where applicable
Assume you are the Test Manager in charge of independent testing for avionics applications.
You are in charge of testing for a project to implement three different CSCI (Computer Software Configuration Item):
-
a BOOT-X CSCI that must be certified at level B of the DO-178B standard
-
a DIAG-X CSCI that must be certified at level C of the DO-178B standard
-
a DRIV-X CSCI that must be certified at level A of the DO-178B standard These are three different software modules written in C language to run on a specific hardware platform. You have been asked to select a single code coverage tool to perform the mandatory code coverage measurements, in order to meet the structural coverage criteria prescribed by the DO- 178B standard. This tool must be qualified as a
verification tool under DO-178B.
Since there are significant budget constraints to purchase this tool, you are evaluating an open- source tool that is able to provide different types of code coverage. This tool meets perfectly your technical needs in terms of the programming
language and the specific hardware platform (it supports also the specific C-compiler).
The source code of the tool is available.
Your team could easily customize the tool to meet the project needs. This tool is not qualified as a verification tool under the DO-178B.
Which of the following are the three main concerns related to that open-source tool selection?
A. Does the tool support all the types of code coverage required from the three levels A, B, C of the DO-178B standard?
B. Does the tool have a good general usability?
C. What are the costs to qualify the tool as a verification tool under the DO-178B?
D. Is the installation procedure of the tool easy?
E. Does the tool require a system with more than 4GB of RAM memory?
F. Is the licensing scheme of the tool compatible with the confidentiality needs of the avionics company?
After a selection process you have selected a test management tool that is going be introduced in your organization and used by your test team in a pilot project.
You have already identified the member of your test team who will be the administrator of the tool, since he/she has a significant experience with the administration of test management tools and so he/she is able to make effective and efficient
up-front decisions about "how" the tool will be used. You have also developed a training plan for the other members of your test team.
In collaboration with the administrator of the tool you have also devised standard ways of managing, storing and maintaining the tool and its assets including backup/restore procedures.
You have also analyzed standard formats supported by the tool (CSV, XLS, XML, etc.) to export, import and archive all the information managed by the tool itself (requirements, test case specifications, test plans etc.) for compliance with the
most important test management tools, in order to minimize the impacts of migrating this information to a new tool that could replace the existing one in the future.
Which of the following phases in the lifecycle of the new tool has NOT been adequately considered in this description?
A. Acquisition
B. Support and maintenance
C. Evolution
D. Retirement
Your test team consists of four members (Mary, Bob, Mark, Dave) with different interpersonal skills.
The following skills assessment spreadsheet shows the characteristics of the team members with respect to a list of interpersonal-skills (for each characteristic only the member with the highest level of that characteristic is indicated and marked with `X'):
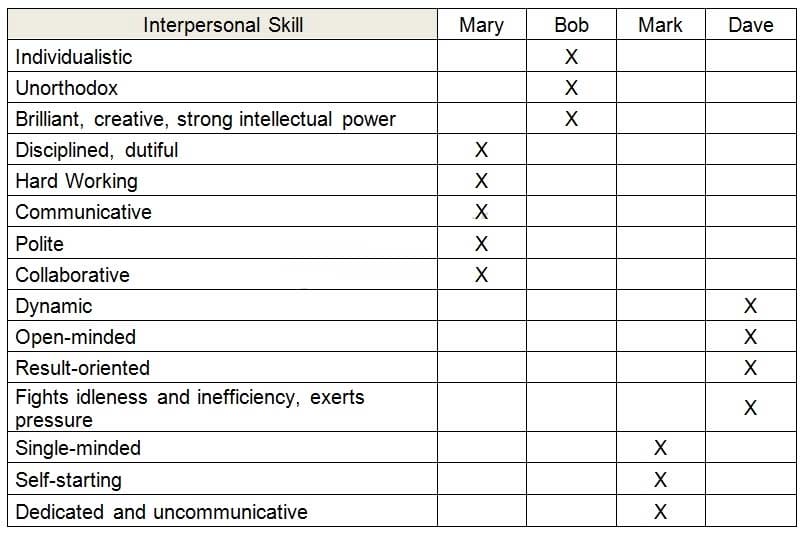
On the next project a member of your test team will have to perform some routine tasks requiring collaboration with other teams. Who in your test team would you expect to be most suitable at doing these tasks?
A. Mary
B. Bob
C. Mark
D. Dave
Which of the following would you expect to be most likely an example of a demotivating factor for testers?
A. The management asks the testers to be kept informed about the intensity, quality and results of testing
B. The testers' recommendations to improve the system or its testability are adopted by the development team
C. The same regressions tests are manually executed by the same testers, for every product release, without regression test tools
D. The testers are assessed on whether and how often they detect important and critical failures
E. Test quality is measured by counting the number of customer/user reported problems.

