C_HANAIMP_17 Online Practice Questions and Answers
You want to control parallelization in a calculation view. Which action is mandatory when you define the parallelization block?
A. Define a union node as the start of the parallelization block.
B. Define a projection node as the end of the parallelization block.
C. Assign tables as the only data sources in the nodes that start the parallelization block.
D. Define a source column as partitioning value in the start node of the parallelization block.
Which of the following are warm tier Solutions? Note: There are 3 correct answers.
A. Active / active read-enabled mode
B. Native Storage Extension
C. Extension Node
D. Dynamic Tiering
E. Persistent Memory
You are querying a calculation view based on the union node, as shown in the graphic. When would the value of the Empty Union Behavior property take effect? Note: There are 2 correct answers to this question.
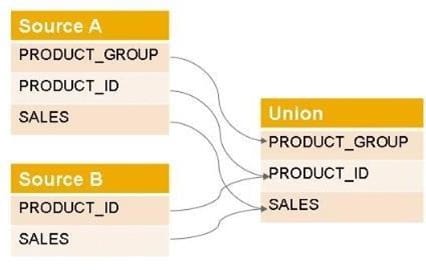
A. When the query requests PRODUCT_GROUP and PRODUCT_ID
B. When the query requests only the PRODUCT_ID
C. When the query requests PRODUCT_GROUP
D. When Source A has no records
You have a calculation view which includes nodes as shown in the graphic. You decide to select the "Ignore Multiple Output for Filters" check box on Projection Node 3. What might the effects of this be?
Note: There are 2 correct answers to this question.
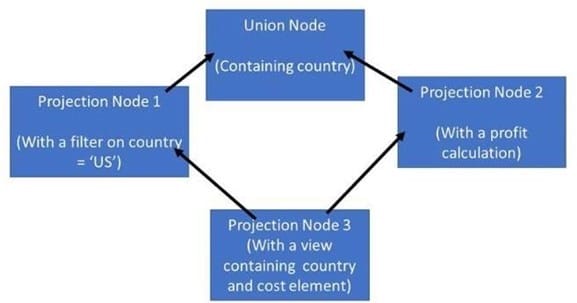
A. The view will return the profit calculation for only the US
B. A change to the data that is returned by the view
C. Increased performance
D. Decreased performance
When would you develop an SQL procedure instead of a function?
A. You need to implement Data Definition Language (DDL) statements.
B. The code should modify data in the table.
C. Optimal performance is apriority.
D. You need to use conditional logic.
E. You want to create a dynamic analytic privilege.
What can you identify using the Performance Analysis Mode?
Note: There are 2 correct answers to this question.
A. Usage statistics of the calculation view
B. Joins that are defined on calculated columns
C. If the data is in the hot or warm storage tier
D. Information about join cardinality
You want to join 2 tables in a calculation view. Why do you use a non-equijoin?
A. The number of joined columns is different in both tables.
B. Join columns do not have the same datatype.
C. The join condition is not represented by matching values.
D. The cardinality is impossible to determine.
In which of the following scenarios would you benefit from enabling table partitioning in SAP HANA?
A. You have a large row store table that is consumed in a view with a variable on COUNTRY column.
B. You have a large column store table that is consumed in a view with a variable on COUNTRY column.
C. You have a dedicated table lo generate the lists of help values for an input parameter.
D. Your stacked model consists of multiple calculation views.
In your calculation view, you need to define a custom data source using SQLScript. In which object do you write your SQL Script?
A. Table function
B. CDS view
C. Procedure
D. Virtual Table
How can you optimize performance when writing SQL for use with calculation views?
Note: There are 2 correct answers to this question.
A. Use declarative language instead of cursors
B. Use calculation engine (CE) functions instead of plain SQL
C. Control the flow logic using IF-THEN-ELSE conditions
D. Increase parallelization by using variables to break up statements

