ACLS Online Practice Questions and Answers
A patient has the following rhythm refractory to adenosine IV and verapamil IV. Before treatment, the heart rate was 200 beats/min and his blood pressure was 110/70 mm Hg. After treatment, the heart rate remains at 200 beats/minute and the blood pressure is 60 mm Hg systolic. What should the immediate treatment be?
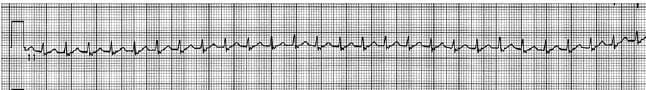
A. atropine 0.5 mg IV
B. dopamine drip IV
C. synchronized cardioversion at 50–100 J
D. verapamil 10 mg IV over 1–2 minutes
Paramedics arrive at the scene and find an unresponsive patient. EMTs have already established an IV and CPR is in progress. There is no pulse. The monitor shows the following rhythm. What should the paramedics do?
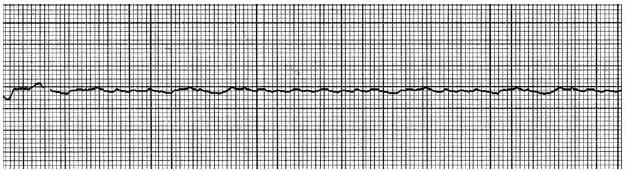
A. immediate defibrillation followed by setup of the automatic external defibrillator
B. administer epinephrine, 1 mL of 1:10,000 solution
C. administer epinephrine, 10 mL of 1:10,000 solution, then defibrillate
D. administer sodium bicarbonate 50 mEq IV bolus
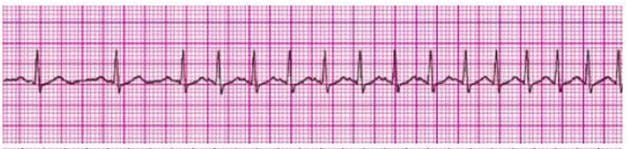
A 45-year-old woman with a history of palpitations develops lightheadedness and palpitations. She has received adenosine 6 mg IV for the rhythm shown above without conversion of the rhythm. She is now extremely apprehensive. Blood pressure is 108/70 mmHg. The next appropriate intervention is
A. Perform vagal maneuvers and repeat adenosine 6 mg IV
B. Perform immediate unsynchronized cardioversion
C. Repeat adenosine 12 mg IV
D. Repeat adenosine 3 mg IV
E. Sedate and perform synchronized cardioversion
A patient is in pulseless ventricular tachycardia. Two shocks and one dose of epinephrine have been given. The next drug/dose to anticipate to administer is
A. Vasopressin 40 U
B. Amiodarone 300 mg
C. Amiodarone 150 mg
D. Epinephrine 3 mg
E. Lidocaine 0.5 mg/kg
A patient with a possible ST-segment elevation Ml has ongoing chest discomfort. Which of the following would be a contraindication to the administration of nitrates?
A. Use of phosphodiesterase inhibitor within 12 hours
B. Left ventricular infarct with bilateral rates
C. Blood pressure greater than 180 mmHg
D. Heart rate 90 per minute
A patient is in cardiac arrest. Ventricular fibrillation has been refractory to an initial shock. Two attempts at peripheral IV access have been unsuccessful. The next recommended access route of administration for the delivery of drugs during CPR is
A. Intraosseous
B. Femoral vein
C. Endotracheal
D. External jugular vein
FILL BLANK
Breath sounds cannot be heard following endotracheal intubation. What is the most likely problem?
A. Esophageal intubation
FILL BLANK
What is the most important goal of ACLS?
A. Restoration of coronary perfusion with subsequent spontaneous cardiac rhythm and preservation of brain function.
SIMULATION
Identify two areas in which a central pulse may be palpated.
A. The carotid artery in the neck or the femoral artery in the groin.
SIMULATION
What adjunctive airways may be necessary to effectively ventilate with the bag-valve-mask?
A. Oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airways.

