9L0-415 Online Practice Questions and Answers
Review the screenshot of part of a Network Utility window, and then answer the question below.
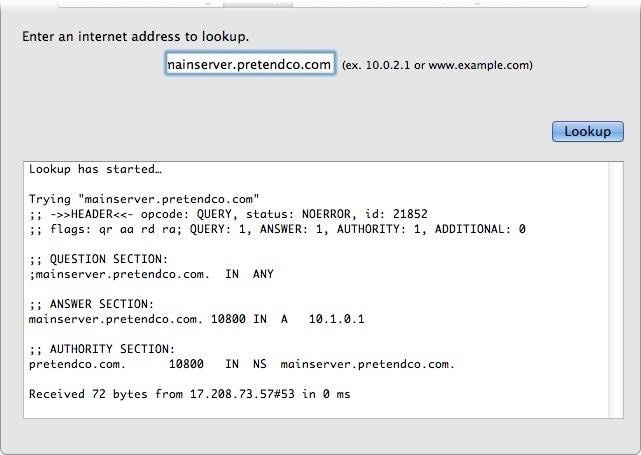
Which statement accurately interprets the Network Utility Lookup results shown above?
A. A forward lookup of mainserver.pretendco.com returned the IP address 10.1.0.1.
B. A reverse lookup of mainserver.pretendco.com returned the IP address 10.1.0.1.
C. A reverse lookup of 10.1.0.1 returned the name mainserver.pretendco.com.
D. The DNS server for mainserver.pretendco.com is pretendco.com.
On your OS X Mountain Lion computer, you want the Finder to display filename extensions by default. How can you configure this setting from the Finder?
A. Choose Preferences from the Finder menu, click Advanced, and select the option "Show all filename extensions."
B. Control-click anywhere on the Desktop, select Preferences from the pop-up menu, click Advanced, and select the option "Show all filename extensions."
C. Choose Show View Options from the View menu, and select the option "Show all filename extensions."
D. Select any file icon, and choose Get Info from the File menu. In the Info window, click the disclosure triangle next to Name and Extension, deselect the option "Hide extension," and click Change All.
A. It is one of three stripes in a RAID set.
B. It is one of three hard disks in a RAID set.
C. It is one of three file systems on a partition.
D. It is one of three partitions on a hard disk.
How do you reset the printing system in OS X Mountain Lion?
A. Open the Print and Scan pane of System Preferences, and delete all of the printers in the Printers list.
B. Navigate to /Library/Printers/ in the Finder, select all items, and move them to the Trash.
C. Open Printer Setup Utility and choose Reset Printing System from the Printer Setup Utility menu.
D. Open the Print and Scan preferences, Control-click in the Printers list, and choose Reset printing system from the shortcut menu.
Which statement is TRUE of file and folder permissions in the Finder in OS X Mountain Lion?
A. A user with Read-only permissions to a folder CANNOT rename any files in that folder.
B. A user with Write-only permissions to a folder can rename any file in that folder.
C. A user with Read-only permissions to a folder CANNOT view any files in that folder.
D. A user with Write-only permissions to a folder can delete any file in that folder.
The OS X Recovery Disk Assistant can create a small OS X Recovery disk that lacks the OS X installation assets. An OS X Installation disk, which includes the full OS X installation assets, can be created by using the createinstallmedia command line tool found inside the Install OS X Mavericks application.
A. What four methods can be used to eject a volume or disk from the Finder?
B. What two methods can be used to create an external OS X Recovery disk?
C. What does OS X use bundles or packages for?
D. What two volume formats are supported for an OS X system volume?
Metadata is information stored outside of a file or folder. It provides additional information about files and folders. Examples include: file flags, extended file attributes, and permissions.
A. How can an OS X system automatically connect to a Wi-Fi network?
B. What's a profile? How are profiles managed?
C. What can you enable to locate a lost Mac system?
D. What is file system metadata? What are some examples of file system metadata?
What Wi-Fi authentication protocols are supported by OS X?
A. The Setup Assistant process guides a user through initial configuration of OS X Mavericks.
B. Disk Utility is the primary application for creating and managing disk images.
C. OS X supports authenticated Wi-Fi via the following authentication protocols: WEP, WPA/WPA2 Personal, and WPA/WPA2 Enterprise, which includes support for 802.1X authentication.
D. OS X supports the following network interfaces and protocols: Ethernet IEEE 802.3 family of hardware network interface standards ?Wireless (Wi-Fi) IEEE 802.11 family of hardware network interface standards FireWire IEEE 1394 bridged network interface Thunderbolt bridged network interface Bluetooth wireless hardware network interface USB connectivity via cellular network adapters or iOS devices with cellular network service Virtual private network (VPN) virtual network interface via the Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) VPN virtual network interface via the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) VPN virtual network interface via Cisco IPSec Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) virtual network interface ?6 to 4 virtual network interface Virtual local area network (VLAN) virtual network interface via the IEEE 802.1Q standard Link Aggregation virtual network interface via the IEEE 802.3ad standard Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), also known as the Internet protocol suite Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Domain Name Service (DNS) protocol Network Basic Input/Output System (NetBIOS) and Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) protocols Authenticated Ethernet via the 802.1X protocol
If a network device needs to send data to another network device on the same LAN, it addresses the outgoing packets based on the destination device's MAC address.
A. How does the IP use the MAC address to send messages between computers on a local area network (LAN)?
B. How do the four default System Preferences categories differ?
C. How does the keychain system help protect your information?
D. How can you verify that DNS host name resolution is working?
AppleTalk works only with OS X v10.5 or earlier.
A. What two volume formats are supported for an OS X system volume?
B. What functionality does OS X support with the AppleTalk protocol?
C. How can you acquire the OS X Mavericks installer?
D. What application is used to manage keychain settings?

