201-01 Online Practice Questions and Answers
What is a benefit that Cascade provides that is not supported by most other network performance management solutions?
A. Identity integration to identify which users are logged into which client machines.
B. Integration with synthetic transaction tools to obtain response time information.
C. A fully functional CLI that is easier to use than a Web based GUI.
D. A Web based GUI that does not require a password or HTTPS connection allowing for easier connection.
When Cascade Pilot is connected to Cascade Shark:
A. Cascade Shark interfaces and captures job traces appear under the devices tab within the sources panel.
B. Cascade Shark interfaces appear under the devices tab of the sources panel AND Cascade Shark capture job traces appear under the files tab of the sources panel.
C. Cascade Shark interfaces and captures job traces appear in the views panel.
D. Cascade Shark interfaces must be selected from the home menu to begin a capture.
Which of the following dashboard widgets is most suitable for monitoring the status of an entire Service, including both front-end and back-end (server-server) segments?
A. Service Health
B. Service Health by Location
C. Watched Applications
D. Current Events
E. System Messages
Authentication mechanisms supported by the Cascade Profiler arE. (Select 2)
A. Local user accounts
B. Active Directory
C. TACACS+
D. RADIUS
E. LDAP
Using the Cascade Active Directory Connector, a Cascade Profiler will be able to see:
A. Attempted Logins only
B. Successful Logins only
C. Failed and Successful Logins
D. Administrator Logins only
Which types of automated analytics are available on Cascade?
A. Application Performance, Interface Performance, and Security.
B. Application Performance, Application Availability, Interface Performance, and Interface Availability.
C. Application Performance, and Interface Performance.
D. Application Performance, Application Availability, Interface Performance, Interface Availability, Service Monitoring and Security.
When using a Network Performance Management tool such as Cascade, the term "drill-down" when troubleshooting usually refers to:
A. Moving from packet headers into packet contents displayed in hexadecimal format
B. The process of logging into the systems GUI to troubleshoot a problem after receiving an email alert
C. Moving from high-level data (such as flow level) down into packet level data
D. Moving from an ARP table on a router to a CAM table on a switch
E. Moving from a flow that is being blocked on the network to a firewall rule that is blocking it
Cascade Shark can be configured to export data to Cascade Profiler. Data exported includes:
A. Flow level information including IP Addresses, number of packets, number of bytes, port/protocol, retransmissions and, when applicable, TCP response time information.
B. Port Statistical information including packet counts, byte counts, checksum error counts, and dropped packet counts.
C. Health information including CPU utilization, up-time, and fan health.
D. Cascade Shark cannot export data to Cascade Profiler.
The exhibit includes a portion of the Cascade Pilot interface and shows:
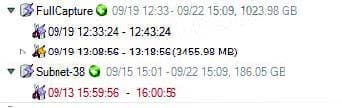
A. Two trace clips, the first has two views applied, the second has one view applied.
B. Two capture job traces, the first has two trace clips associated with it, the second has one trace clip associated with it.
C. Two Cascade Shark appliances, the first has two capture jobs, the second has one capture job.
D. Two packet capture (pcap) files, the first has two trace clips associated with it, the second has one trace clip associated with it.
Which component of Cascade can be used with a Cascade Express Profiler?
A. Standard or Enterprise Profiler
B. Gateways
C. Sensor
D. Shark
E. Sensor-VE
F. All of the above

