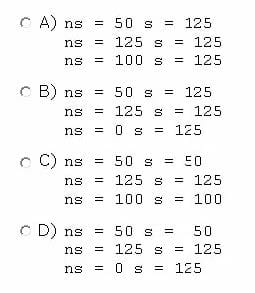1Z0-808 Online Practice Questions and Answers
A method is declared to take three arguments. A program calls this method and passes only two arguments. What is the results?
A. Compilation fails.
B. The third argument is given the value null.
C. The third argument is given the value void.
D. The third argument is given the value zero.
E. The third argument is given the appropriate falsy value for its declared type. F) An exception occurs when the method attempts to access the third argument.
Given:
public class Painting {
private String type;
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Painting obj1 = new Painting();
Painting obj2 = new Painting();
obj1.setType(null);
obj2.setType("Fresco");
System.out.print(obj1.getType() + " : " + obj2.getType());
}
}
What is the result?
A. : Fresco
B. null : Fresco
C. Fresco : Fresco
D. A NullPointerException is thrown at runtime
Given the code fragment Which code fragments, inserted independently, enable the code compile?
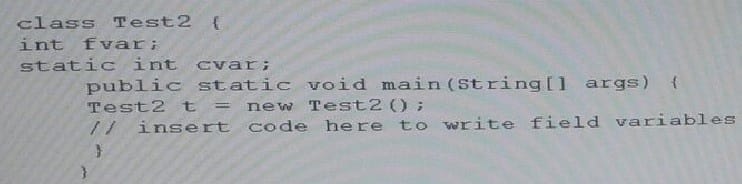
A. t.fvar = 200;
B. cvar = 400;
C. fvar = 200; cvar = 400;
D. this.fvar = 200; this.cvar = 400;
E. t.fvar = 200; Test2.cvar = 400;
F. this.fvar = 200; Test2.cvar = 400;
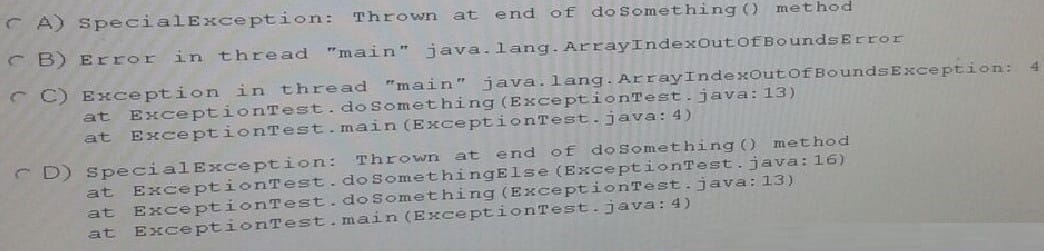
Given:
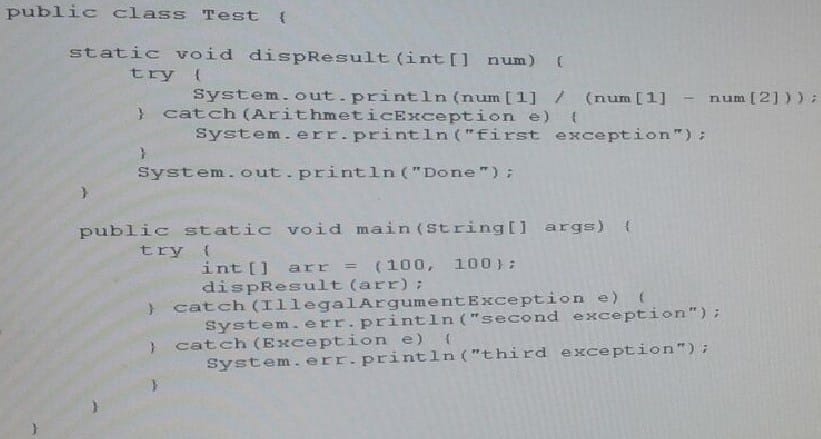
What is the result?
A. 0 Done
B. First Exception Done
C. Second Exception
D. Done Third Exception
E. Third Exception
Given the code fragment:

What is the result?
A. 1 3 5 7 1 3
B. 1 2 1 3
C. 1 3 1 3 0 0
D. 1 3 followed by an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
E. Compilation fails.
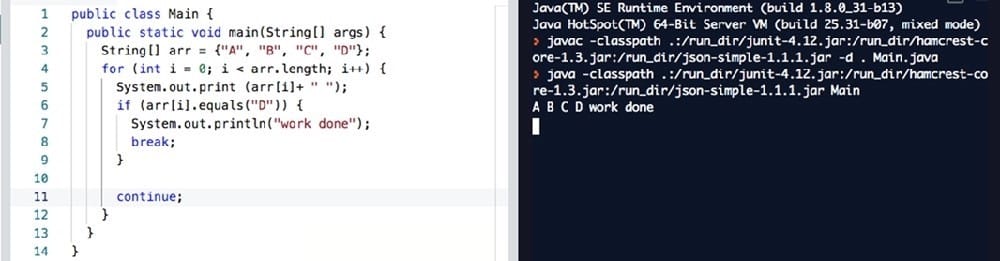
Given the code fragment:

Which code fragment, when inserted at line n1, enables the App class to print Equal?

A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D